- Published on
Falco를 활용하여 Terminal Shell 명령어 로그 수집하기
- Authors
- Name
- Jay
Kubernetes에서 Worker Node나 Pod에 Shell로 접근하면 기록을 남기고, 원하는 경우에는 알림을 받고 싶었다. 그래서 CNCF 졸업한 프로젝트인 Falco를 통해서 원하는 시스템을 만들 수 있을지 확인해보았다. Falco Architecture가 문서에 아래 그림과 함께 친절히 설명되어 있다.
Falco operates in both kernel and user space. In kernel space, Linux system calls (syscalls) are collected by a driver, for example, the Falco kernel module or Falco eBPF probe. Next, syscalls are placed in a ring buffer from which they are moved into user space for processing. The events are filtered using a rules engine with a Falco rule set.
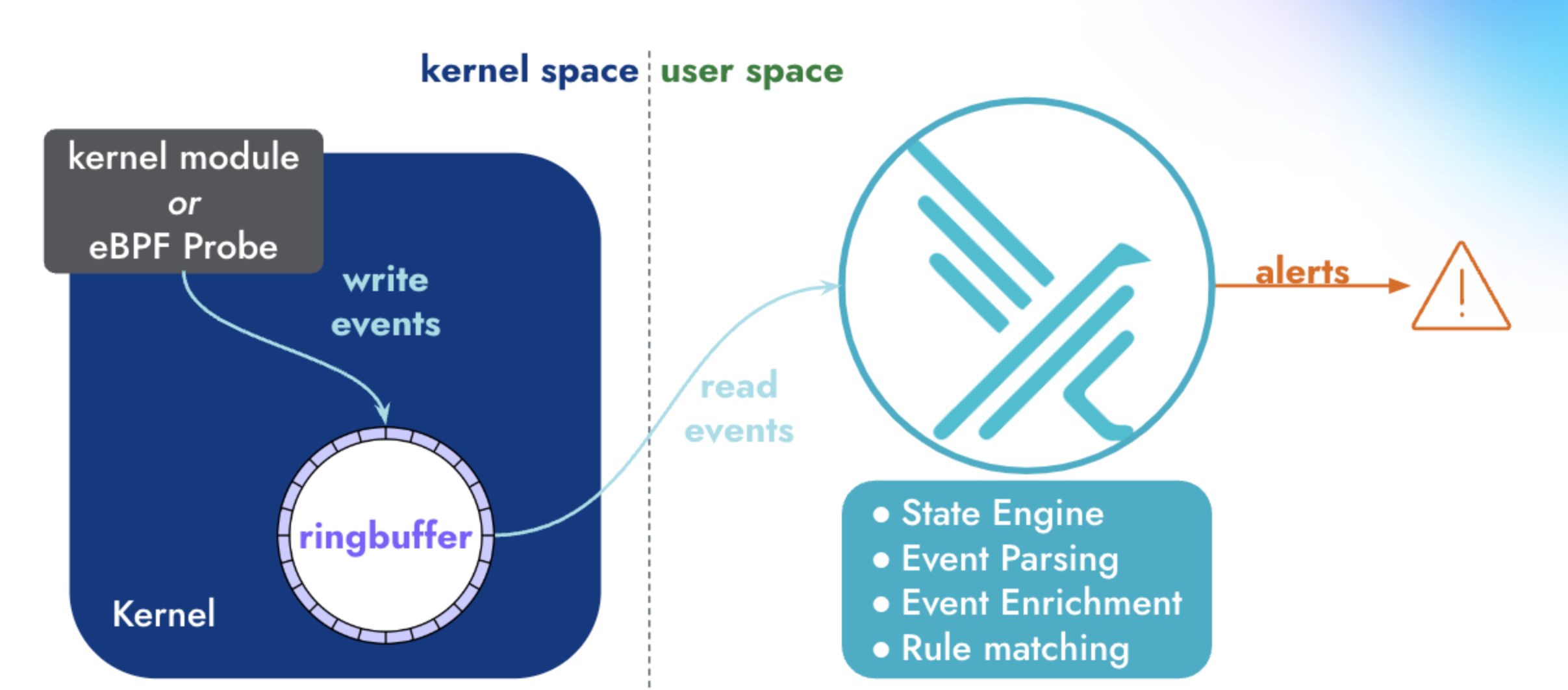
Falco는 Rule을 통해서 선택적으로 이벤트를 저장하는 구조로 되어 있다. 정의된 Falco Rule로 filter된 이벤트를 Standard Output, File Output, Syslog Output, Program Output, HTTP/HTTPS Output, JSON Output등을 통해서 원하는 Output 형식을 정의할 수 있다. Syslog Output의 경우에는 Falco를 Host에 직접 설치하였을 때, Syslog Service를 통해서 남기는 것으로 보인다.. Kubernetes에서 Pod로 Falco를 실행할 때는 Standard Output을 사용하고, Fluentbit이나 Opentelemetry Filelog Receiver등으로 file을 tail해서 저장할 수 있다.
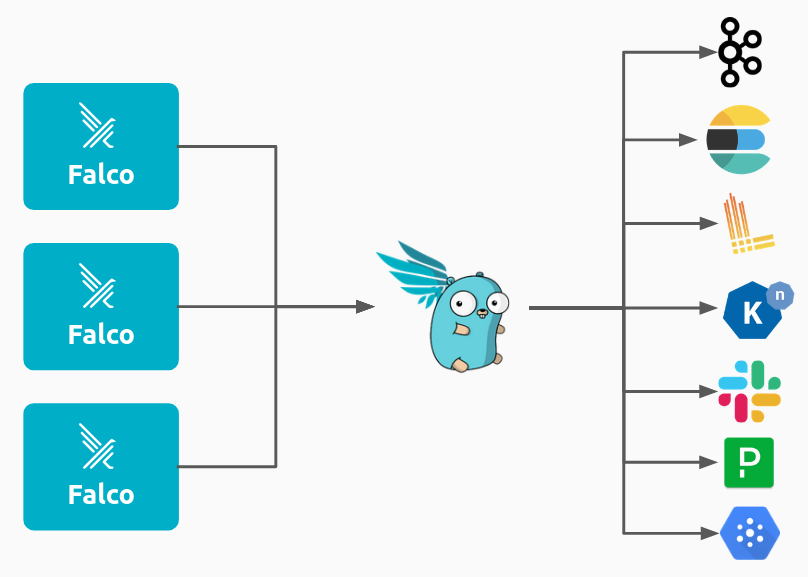
또한 Falcosidekick을 통해서 Forwarding을 통해서 원하는 곳에 Falco Alert를 전달할 수 있다. 아래는 공식문서에 있는 그림으로 Falcosidekick을 통해서 편하게 다양한 시스템에 전달할 수 있다. Loki에 push하여 log를 저장할 수도 있고, Slack에 메세지를 보낼 수도 있다. 이 방법은 Falco HTTP/HTTPS Output을 통해서 Falcosidekick에게 Alert를 전송하는 것이다.
Helm으로 설치
Helm Chart를 이용하여 Falco를 설치한다.
helm repo add falcosecurity https://falcosecurity.github.io/charts
helm repo update
$ helm search repo falcosecurity
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION
falcosecurity/event-generator 0.3.3 0.10.0
falcosecurity/falco 4.3.0 0.37.1
falcosecurity/falco-exporter 0.10.0 0.8.3
falcosecurity/falcosidekick 0.7.17 2.28.0
falcosecurity/k8s-metacollector 0.1.7 0.1.0
Kernel module대신에 performance적으로 유리한 ebpf를 사용해서 syscall을 probe하도록 한다. 그리고 falcosidekick을 같이 설치하기 위해서 enabled을 true로 설정해주고, loki와 slack에 Falco alert를 전달하도록 설정하였다. Falco에서는 EMERGENCY, ALERT, CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, NOTICE, INFORMATIONAL, DEBUG 순으로 우선순위 정보를 정의할 수 있다. minimumpriority를 통해서 어느 우선순위까지 보낼것인지 정의를 할 수 있는데, 아래에서는 alert로 설정했기 때문에 EMERGENCY와 ALERT에 대해서 메세지를 전달받게 된다. falcosidekick의 slack 설정은 이 문서에서 확인 가능하다.
values.yaml
driver:
kind: ebpf
falcosidekick:
enabled: true
config:
loki:
hostport: http://loki:3100
tenant: falco
slack:
webhookurl: https://hooks.slack.com/services/{something}
minimumpriority: alert
outputformat: fields
Helm Chart의 value는 기본값으로 아래와 같이 stdout_output이 enable되어 있다. 따라서 Daemonset으로 설치되는 Falco의 container log를 보면 Falco rule에 따른 event들이 남아 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
stdout_output:
enabled: true
정의한 values.yaml을 통해서 Helm Chart를 배포한다.
helm install falco falcosecurity/falco \
--create-namespace \
--namespace falco \
--values values.yaml
설치과 완료되면 아래와 같이 falco의 설정값들이 ConfigMap에 정의된다.
$ kubectl get cm -n falco
NAME DATA AGE
falco 1 1d
falco-falcoctl 1 1d
falco-rules 1 1d
kubectl get cm falco -o yaml으로 확인해보면 아래와 같이 json 형식의 output이 설정되게 된다. 그리고 falco-facosidekick ClusterIP 서비스로 요청하도록 http_output이 설정되고, stdout_output도 동일하게 true로 설정된다.
json_output: true
http_output:
ca_bundle: ""
ca_cert: ""
ca_path: /etc/falco/certs/
client_cert: /etc/falco/certs/client/client.crt
client_key: /etc/falco/certs/client/client.key
compress_uploads: false
echo: false
enabled: true
insecure: false
keep_alive: false
mtls: false
url: http://falco-falcosidekick:2801
user_agent: falcosecurity/falco
stdout_output:
enabled: true
Falco Rule
Falco rules을 기본적으로 stable 상태에 있는 rule들 자동으로 설정이 된다. Community에서 관리되는 rule들은 여기에서 확인할 수 있다. incubating, sandbox 상태의 rule도 추가하고 싶으면 Helm Chart Value에 정의하여 추가할 수 있다.
stable 상태의 rule들은 Github Repo의 falco_rules.yaml에서도 확인할 수 있다. 예를 들어서 falco_rules.yaml에서 아래와 같은 Rule이 정의되어 있다. macro는 다시 재사용할 수 있도록 특정한 조건들을 정의해 놓는 것이고, list를 통해서 여러 개의 값을 묶어서 정의할 수 있다. Terminal shell in container에서 macro와 list를 사용해서 정의하고 있다.
- macro: spawned_process
condition: (evt.type in (execve, execveat) and evt.dir=<)
- macro: container
condition: (container.id != host)
- macro: container_entrypoint
condition: (not proc.pname exists or proc.pname in (runc:[0:PARENT], runc:[1:CHILD], runc, docker-runc, exe, docker-runc-cur, containerd-shim, systemd, crio))
- macro: user_expected_terminal_shell_in_container_conditions
condition: (never_true)
- list: shell_binaries
items: [ash, bash, csh, ksh, sh, tcsh, zsh, dash]
- macro: shell_procs
condition: (proc.name in (shell_binaries))
- rule: Terminal shell in container
desc: >
A shell was used as the entrypoint/exec point into a container with an attached terminal. Parent process may have
legitimately already exited and be null (read container_entrypoint macro). Common when using "kubectl exec" in Kubernetes.
Correlate with k8saudit exec logs if possible to find user or serviceaccount token used (fuzzy correlation by namespace and pod name).
Rather than considering it a standalone rule, it may be best used as generic auditing rule while examining other triggered
rules in this container/tty.
condition: >
spawned_process
and container
and shell_procs
and proc.tty != 0
and container_entrypoint
and not user_expected_terminal_shell_in_container_conditions
output: A shell was spawned in a container with an attached terminal (evt_type=%evt.type user=%user.name user_uid=%user.uid user_loginuid=%user.loginuid process=%proc.name proc_exepath=%proc.exepath parent=%proc.pname command=%proc.cmdline terminal=%proc.tty exe_flags=%evt.arg.flags %container.info)
priority: NOTICE
tags: [maturity_stable, container, shell, mitre_execution, T1059]
이제 Pod에 접근하면
kubectl exec -it nginx-pod -- /bin/sh
아래와 같은 log가 남게 된다.
{
"hostname": "node-name",
"output": "10:31:35.913486795: Notice A shell was spawned in a container with an attached terminal (evt_type=execve user=root user_uid=0 user_loginuid=-1 process=sh proc_exepath=/usr/bin/dash parent=containerd-shim command=sh terminal=34816 exe_flags=EXE_WRITABLE container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_image=docker.io/library/nginx container_image_tag=latest container_name=nginx k8s_ns=default k8s_pod_name=pod-name)",
"priority": "Notice",
"rule": "Terminal shell in container",
"source": "syscall",
"tags": ["T1059", "container", "maturity_stable", "mitre_execution", "shell"],
"time": "2024-05-03T10:31:35.913486795Z",
"output_fields": {
"container.id": "6fec6323ae4c",
"container.image.repository": "docker.io/library/nginx",
"container.image.tag": "latest",
"container.name": "nginx",
"evt.arg.flags": "EXE_WRITABLE",
"evt.time": 1714732295913486795,
"evt.type": "execve",
"k8s.ns.name": "default",
"k8s.pod.name": "pod-name",
"proc.cmdline": "sh",
"proc.exepath": "/usr/bin/dash",
"proc.name": "sh",
"proc.pname": "containerd-shim",
"proc.tty": 34816,
"user.loginuid": -1,
"user.name": "root",
"user.uid": 0
}
}
테스트를 한 환경의 Container Runtime이 containerd이기 때문에, parent process명은 containerd-shim으로 표시가 된다. evt.type는 syscall event을 가지는데, 공식문서에서 지원하는 events 종류를 확인할 수 있다. execve는 프로그램을 실행할 때의 syscall인데, /usr/bin/dash binary file이 실행되었기 때문에 evt.type은 execve가 되고 proc.exepath가 usr/bin/dash가 된다. 그리고 아래처럼 문서에 syscall이 불렸을 때 >, 끝났을 때 <로 표시하게 된다. >는 filepath로 실행하고, <는 systemcall이 끝나고 기타 정보들을 반환한다.

Custom Rule
기본으로 설정되어 있는 Rule을 살펴보았고, marcro, list, rule Syntax로 원하는 custom rule을 설정할 수 있다. accept, listen은 < 에서 fd params을 가지고, recvfrom, recvmsg는 >에서 fd params를 가지고 있다. 이제 params fd를 통해서 fd.sport Server Port가 22인지 확인한다. 이 조건을 만족하면 output으로 fd.cip client IP address와 fd.cport client Port 값을 남기도록 하였다.
custom-rules.yaml
customRules:
rules-ssh.yaml: |-
- list: ssh_standard_ports
items: [22]
- macro: ssh_standard_ports_network
condition: (fd.sport in (ssh_standard_ports))
- rule: Inbound SSH Connection
desc: Detect Inbound SSH Connection
condition: >
((evt.type in (accept,listen) and evt.dir=<) or
(evt.type in (recvfrom,recvmsg))) and ssh_standard_ports_network
output: >
Inbound SSH connection (user=%user.name client_ip=%fd.cip client_port=%fd.cport server_ip=%fd.sip)
priority: ALERT
tags: [network]
정의한 costom rule을 아래와 같이 적용한다.
helm upgrade falco falcosecurity/falco \
-f ./custom-rules.yaml \
--namespace falco \
--values values.yaml
custom rule에 의해서 아래와 같이 log가 남는다. 그리고 container.id가 host이기 때문에 Kubernetes 관련된 정보는 <NA>로 표시된다.
{
"hostname": "node-name",
"output": "11:37:53.059395044: Alert Inbound SSH connection (user=root client_ip=x.x.x.x client_port=56483 server_ip=x.x.x.x) container_id=host container_image=<NA> container_image_tag=<NA> container_name=host k8s_ns=<NA> k8s_pod_name=<NA>",
"priority": "Alert",
"rule": "Inbound SSH Connection",
"source": "syscall",
"tags": ["network"],
"time": "2024-05-03T11:37:53.059395044Z",
"output_fields": {
"container.id": "host",
"container.image.repository": null,
"container.image.tag": null,
"container.name": "host",
"evt.time": 1714736273059395044,
"fd.cip": "x.x.x.x",
"fd.cport": 56483,
"fd.sip": "x.x.x.x",
"k8s.ns.name": null,
"k8s.pod.name": null,
"user.name": "root"
}
}
그리고 위에서 falcosidekick에서 slack도 설정을 했기 때문에 아래처럼 슬랙 메세지가 오게 된다.
원하는 결과
최종적으로 Falco로 구현하고 싶은 것은 Worker Node나 Pod의 Container에 Terminal shell로 연결했을 때, 모든 명령어들을 저장하고 알림을 필요시에 받고 싶다.
Falco는 Rule을 통해서 특정 조건에 해당되는 Event를 저장하는 구조로 되어있다. 따라서 이렇게 모든 명령어들을 저장하고 싶다면, 그렇게 할 수 있도록 Custom Rule을 정의해야 한다.
- rule: shell_in_container
desc: notice shell activity within a container
condition: >
evt.type = execve and
evt.dir = < and
container.id != host and
proc.pname = sh
output: >
shell in a container
(user=%user.name container_id=%container.id container_name=%container.name
shell=%proc.name parent=%proc.pname cmdline=%proc.cmdline)
priority: WARNING
ls의 경우에는 execve가 사용되고 아래처럼 log가 남게 된다.
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-pod -- /bin/sh
# ls
{
"hostname": "node-name",
"output": "12:03:52.176355678: Warning shell in a container (user=root container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_name=nginx shell=ls parent=sh cmdline=ls /bin) container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_image=docker.io/library/nginx container_image_tag=latest container_name=nginx k8s_ns=default k8s_pod_name=pod-name",
"priority": "Warning",
"rule": "shell_in_container",
"source": "syscall",
"tags": [],
"time": "2024-05-03T12:03:52.176355678Z",
"output_fields": {
"container.id": "6fec6323ae4c",
"container.image.repository": "docker.io/library/nginx",
"container.image.tag": "latest",
"container.name": "nginx",
"evt.time": 1714737832176355678,
"k8s.ns.name": "default",
"k8s.pod.name": "pod-name",
"proc.cmdline": "ls /bin",
"proc.name": "ls",
"proc.pname": "sh",
"user.name": "root"
}
}
Pod container말고 host를 하고 싶다면 Condition에서 container.id = host로 설정할 수 있다. 동일한 방식으로 rule을 추가하면 다양한 명령어들이 Shell을 통해서 실행되고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- rule: shell_in host
desc: notice shell activity within a host
condition: >
evt.type = execve and
evt.dir = < and
container.id = host and
proc.pname = sh
output: >
shell in a host
(user=%user.name shell=%proc.name parent=%proc.pname cmdline=%proc.cmdline)
priority: WARNING
그런데 mkdir의 경우에는 evt.type = mkdir로 추가해줘야한다. 따라서 condition에서 in으로 mkdir도 추가한다.
- rule: shell_in_container
desc: notice shell activity within a container
condition: >
evt.type in (execve, mkdir) and
evt.dir = < and
container.id != host and
proc.pname = sh
output: >
shell in a container
(user=%user.name container_id=%container.id container_name=%container.name
shell=%proc.name parent=%proc.pname cmdline=%proc.cmdline)
priority: WARNING
그러면 이제 mkdir도 아래처럼 로그가 남는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-pod -- /bin/sh
# mkdir /hellofalco
{
"hostname": "node-name",
"output": "20:29:06.389110693: Warning shell in a container (user=root container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_name=nginx shell=mkdir parent=sh cmdline=mkdir /hellofalco) container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_image=docker.io/library/nginx container_image_tag=latest container_name=nginx k8s_ns=default k8s_pod_name=pod-name",
"priority": "Warning",
"rule": "shell_in_container",
"source": "syscall",
"tags": [],
"time": "2024-05-03T20:29:06.389110693Z",
"output_fields": {
"container.id": "6fec6323ae4c",
"container.image.repository": "docker.io/library/nginx",
"container.image.tag": "latest",
"container.name": "nginx",
"evt.time": 1714768146389110693,
"k8s.ns.name": "default",
"k8s.pod.name": "pod-name",
"proc.cmdline": "mkdir /hellofalco",
"proc.name": "mkdir",
"proc.pname": "sh",
"user.name": "root"
}
}
하지만 echo "hello world" > example.txt 명령어를 했을 때는 위의 Rule에 포함되지 않는다. 따라서 아래처럼 추가해본다.
- rule: shell_in_container
desc: notice shell activity within a container
condition: >
evt.type in (open, openat, openat2) and
evt.dir = < and
fd.filename in (example.txt) and
container.id != host
output: >
shell in a container
(file=%fd.name evt_type=%evt.type user=%user.name container_id=%container.id container_name=%container.name
shell=%proc.name parent=%proc.pname cmdline=%proc.cmdline)
priority: WARNING
이제 example.txt를 아래와 같이 echo로 생성해본다.
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-pod -- /bin/sh
# echo "hello world" > example.txt
그러면 fd.name을 통해서 수정된 파일명을 알 수 있다. 하지만 echo "hello world" > example.txt 전체 명령어를 남길 방법이 보이지 않는다. 🤔 그리고 open의 경우에는 너무나 많은 프로세스에서 call하고 있기 때문에 좀더 구체적인 조건을 작성하지 않으면 불필요하게 너무 많은 이벤트 로그가 남게 된다. Falco stable Rule 중에 /var/log/auth.log나 /var/log/syslog처럼 시스템 로그들을 수정하면 알림이 오도록 설정되어 있다. 이처럼 구체적인 조건을 통해서 특정 행위에 대한 이벤트를 발생시킨다.
{
"hostname": "node-name",
"output": "21:41:34.978625505: Warning shell in a container (file=/example.txt evt_type=openat user=root container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_name=nginx shell=sh parent=containerd-shim cmdline=sh) container_id=6fec6323ae4c container_image=docker.io/library/nginx container_image_tag=latest container_name=nginx k8s_ns=default k8s_pod_name=pod-name",
"priority": "Warning",
"rule": "shell_in_container",
"source": "syscall",
"tags": [],
"time": "2024-05-03T21:41:34.978625505Z",
"output_fields": {
"container.id": "6fec6323ae4c",
"container.image.repository": "docker.io/library/nginx",
"container.image.tag": "latest",
"container.name": "nginx",
"evt.time": 1714772494978625505,
"evt.type": "openat",
"fd.name": "/example.txt",
"k8s.ns.name": "default",
"k8s.pod.name": "pod-name",
"proc.cmdline": "sh",
"proc.name": "sh",
"proc.pname": "containerd-shim",
"user.name": "root"
}
}
결론
Kubernetes Worker Node와 Pod Container에 직접 Terminal shell을 통해서 어떠한 명령어들을 실행했을 때, 그것들을 모두 저장하고 특정한 조건에 따라 실시간 알림을 보내고 싶었다. Falco는 Rule 정의를 통해서 선택적으로 Kernel event를 보안 위협이 되는 이벤트를 저장하고 실시간성으로 알림을 보낼 수 있다. 따라서 Falco Rule을 정의하여 sh, bash등이 Parent Process로 있으면서 ls, cat등을 execve syscall로 실행할 때 event를 수집하도록 하였다. 하지만 mkdir 명령어에 대해서 mkdir이나 mkdirat 조건을 추가 해줘야 한다. echo "hello world" > example.txt의 경우에는 example.txt를 수정/삭제할 때 이벤트를 남길 수 있지만, 전체 shell에서 실행한 전체 명령어를 남기는 방법이 보이지 않았다. 그리고 너무 많은 곳에서 파일을 읽고 쓰기 때문에 필터 조건을 구체적으로 설정하지 않으면 원하지 않은 이벤트들이 너무 많이 남게 된다. 따라서 내가 원하던 구현을 위해서 Falco는 적합하지 않다는 결론을 내리게 되었다.
그러면 원하는 구현에 더 적합한 다른 오픈소스 소프트웨어가 있을까? 🧐